SQLite Local Database Guide: Build Apps with Zero Database Hassle
Master SQLite – the serverless database engine powering millions of apps. Learn setup, real-world examples, best practices & when to use it. Perfect for mobile & local storage. Start building today!
Hey there, coders and creators! 👋 Ever found yourself building an app and thinking, "Man, I just need a simple way to store data locally without setting up a whole database server?" Or maybe you're working on a mobile app, a desktop tool, or even a small web project and need something lightweight yet powerful? Well, pull up a chair, grab your favorite drink, and let's talk about SQLite – the unassuming database that's probably running on more devices than you realize.
What the Heck is SQLite Anyway?
Let's break it down without the tech jargon overload. SQLite is a serverless, self-contained, zero-configuration SQL database engine. Sounds fancy, but what does that actually mean?
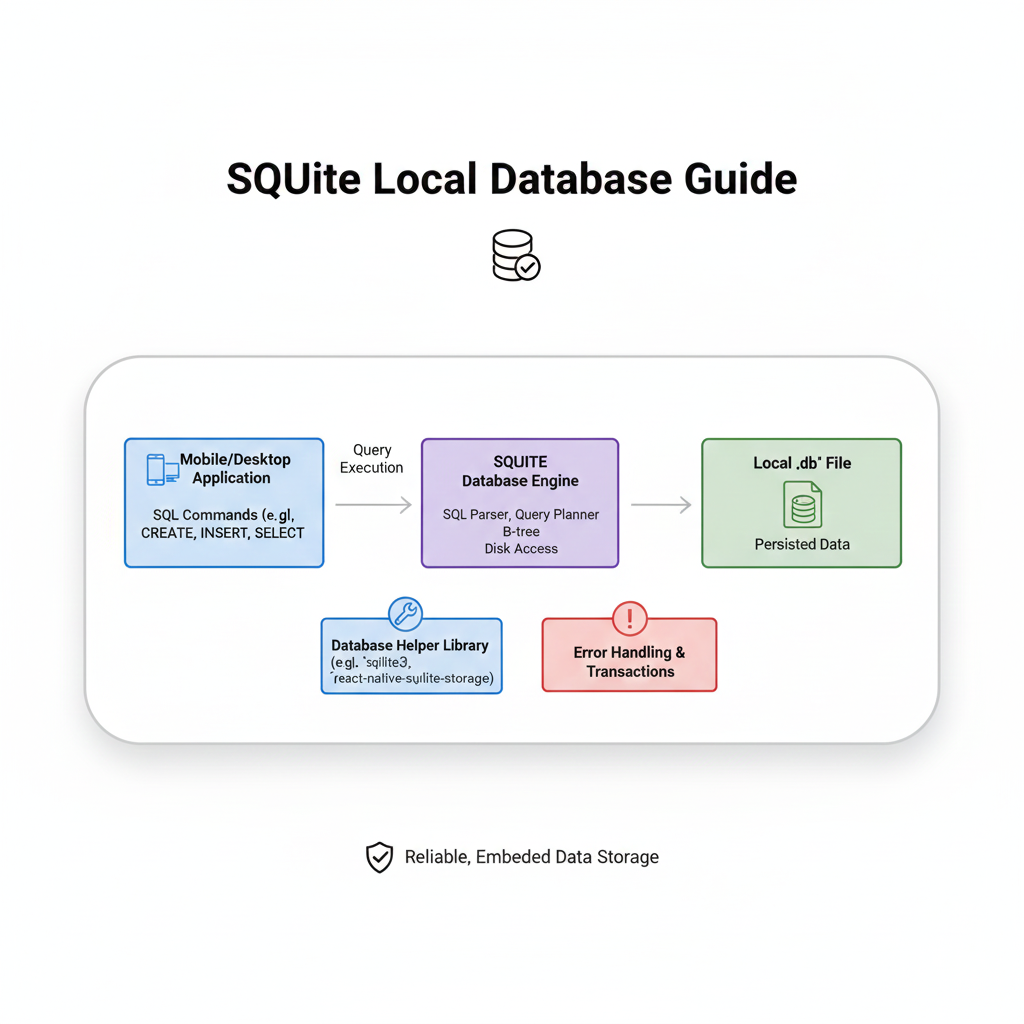
Imagine a regular database like MySQL or PostgreSQL as a massive, shared library that needs a full-time librarian (the server) to manage it. Now picture SQLite as a personal notebook you carry in your pocket. You can write in it, read from it, organize it – all without needing that librarian. The entire database is just a single file on your disk. That's it. One file.
The "serverless" part means there's no separate server process to install, configure, or manage. The "self-contained" bit means everything you need is in that single file or library. And "zero-configuration"? You literally just use it. No "sudo service mysql start" nonsense.
Real talk: SQLite is everywhere. Your Android or iPhone apps use it to store local data. Your browser might use it for cookies and cache. Even your smart TV or car's infotainment system probably has SQLite running somewhere in the background. It's the silent workhorse of the software world.
Why Should You Care About SQLite in 2024?
In today's development landscape where we're building everything from Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) to cross-platform mobile apps and IoT devices, SQLite solves some very real problems:
Offline-First Apps: Users expect apps to work without internet. SQLite lets you store data locally and sync when connected.
Prototyping Speed: Need to test a database schema? SQLite lets you spin up in seconds, not hours.
Embedded Systems: Limited resources? SQLite runs on basically anything with a processor.
Testing: Run your tests with a real database without mocking everything out.
Let's Get Our Hands Dirty: SQLite in Action
Enough theory – let's see some code! The beautiful thing about SQLite is how ridiculously simple it is to get started.
Setting Up: It's Easier Than You Think
For Python developers (which, let's be honest, is most of us these days):
python
import sqlite3
# That's it. No installation, no configuration.
# It's built into Python's standard library!
# Connect to a database (creates it if it doesn't exist)
conn = sqlite3.connect('my_app.db')
# Create a cursor object
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Create a table
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
username TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
email TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
# Insert some data
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users (username, email) VALUES (?, ?)",
('tech_guru', 'guru@example.com'))
# Save (commit) the changes
conn.commit()
# Query data
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = cursor.fetchall()
for user in users:
print(user)
# Don't forget to close the connection!
conn.close()For Node.js/JavaScript folks:
javascript
const sqlite3 = require('sqlite3').verbose();
// Open a database connection
let db = new sqlite3.Database('./my_app.db', (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err.message);
}
console.log('Connected to the SQLite database.');
});
// Run SQL commands
db.run(`CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
price REAL
)`);
// Insert data
db.run(`INSERT INTO products(name, price) VALUES(?, ?)`,
['Awesome Product', 29.99], function(err) {
if (err) {
return console.log(err.message);
}
console.log(`A row has been inserted with rowid ${this.lastID}`);
});
// Query data
db.each(`SELECT * FROM products`, (err, row) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(`${row.id}: ${row.name} - $${row.price}`);
});
// Close the connection
db.close();See? No "npm install massive-database-server" needed. It's refreshingly straightforward.
Real-World Projects Where SQLite Shines
Let me tell you about some actual use cases where SQLite is absolutely killing it:
Mobile Apps: That fitness app tracking your daily steps? Probably SQLite. Your note-taking app saving drafts locally? Likely SQLite. Instagram even uses it for caching on Android!
Desktop Applications: Think VS Code, Adobe Lightroom, or even financial software like TurboTax. They use SQLite to store everything from user preferences to complex application data.
Web Browsers: Chrome, Firefox, Safari – they all use SQLite internally for storing history, bookmarks, and other metadata.
Embedded Systems: Smart home devices, car systems, IoT sensors – anywhere with limited resources but a need for structured data storage.
Development & Testing: This is where I use it daily. Need to test a database interaction? Mock services with SQLite. Building a prototype? SQLite gets you moving in minutes, not hours.
Best Practices: Don't Just Wing It
Even though SQLite is simple, you should still follow some best practices:
Use Parameterized Queries (Always!)
python
# GOOD cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES (?)", (username,)) # BAD (SQL injection vulnerability!) cursor.execute(f"INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('{username}')")Handle Transactions Properly
python
# Use context managers for automatic commit/rollback with sqlite3.connect('app.db') as conn: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute("INSERT INTO ...") # No need to manually commit - it's automatic!Enable Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) for Better Concurrency
python
conn = sqlite3.connect('app.db') conn.execute('PRAGMA journal_mode=WAL') # Magic line for performance!Backup Your Database File
Since it's just a file, backing up is as simple as copyingmy_app.dbto another location. But do it when the database isn't being written to!Use Connection Pooling in Web Apps
If you're using SQLite in a web application (like Flask or Express), don't open and close connections on every request. Use connection pooling.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
"My app is slow when multiple users write at once!"
SQLite uses file-level locking by default. For high-concurrency web apps, consider WAL mode (mentioned above) or, honestly, consider if you've outgrown SQLite. It's amazing, but it's not PostgreSQL.
"I deleted my database file accidentally!"
Your database is literally just a file. Treat it like any important file – back it up regularly. Use version control for schema changes.
"How do I handle migrations?"
Tools like Alembic (Python) or knex.js (Node.js) work beautifully with SQLite. Or roll your own simple migration system with version numbers in a table.
SQLite vs. The World: When to Use What
SQLite vs. MySQL/PostgreSQL: Use SQLite for local storage, embedded apps, or single-user applications. Use server databases for multi-user web apps with high concurrent writes.
SQLite vs. NoSQL (MongoDB, etc.): If your data is relational and structured, SQLite often makes more sense. If you're dealing with constantly changing, document-like data, NoSQL might be better.
SQLite vs. LocalStorage (in browsers): LocalStorage is for simple key-value pairs (max ~5-10MB). SQLite (via WebSQL or compiled to WebAssembly) is for complex, queryable data.
FAQs: Stuff You're Probably Wondering
Q: Can SQLite handle millions of records?
A: Absolutely. It's been tested with hundreds of gigabytes of data. The limiting factor is usually disk I/O, not SQLite itself.
Q: Is SQLite ACID-compliant?
A: Yes! Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability – all checked. Your data is safe.
Q: Can I use it in production web apps?
A: For low-to-medium traffic sites (think <100k hits/day), absolutely. The official SQLite website (sqlite.org) uses SQLite and handles millions of hits. But for high-concurrency apps with many simultaneous writers, consider a client-server database.
Q: What about encryption?
A: The core SQLite doesn't include encryption, but there are extensions like SQLCipher that add AES-256 encryption.
Q: How do I view my SQLite data visually?
A: Tools like DB Browser for SQLite (free), TablePlus, or even VS Code extensions make browsing your data a breeze.
Wrapping Up: Your New Secret Weapon
SQLite is one of those technologies that quietly powers so much of our digital world while being simple enough that you can master it in an afternoon. It's the perfect tool for local storage, prototyping, embedded systems, and even certain production applications.
Whether you're building a mobile app, a desktop tool, or just need a simple way to persist data in your project, SQLite deserves a spot in your toolkit. It's reliable, battle-tested, and beautifully simple.
Remember, the best tool isn't always the most complex one – sometimes it's the one that just works without drama. And SQLite? It definitely just works.
Want to build more projects with SQLite and other in-demand technologies? Level up your skills with professional, industry-focused training. To learn professional software development courses such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. We'll help you go from SQLite basics to building complete, production-ready applications.
Got questions about SQLite or want to share how you're using it? Drop a comment below! And if you found this guide helpful, share it with a fellow developer who's wrestling with database choices. Happy coding! 🚀


















