React Native for IoT: Building Cross-Platform Smart Device Apps
Can you use React Native for IoT devices? Absolutely! Discover how to build powerful, cross-platform mobile apps to control your smart home, wearables, and industrial sensors. Learn the pros, cons, real-world use cases, and best practices. Master app development with courses at CoderCrafter.in!
React Native for IoT: Your Phone as the Ultimate Remote Control
Let's be real. Our world is getting smarter by the minute. It’s not just about phones and laptops anymore. Your lightbulb syncs with the sunrise, your fridge can guilt-trip you about expired milk, and your watch is probably judging your sleep schedule. This is the Internet of Things (IoT), and it’s everywhere.
But here’s the catch: every smart device needs a way to talk to us, the users. And 9 times out of 10, that “way” is a mobile app. Now, if you're a business building a smart device, you face a classic developer dilemma: Do you build a native iOS app with Swift? A native Android app with Kotlin? That means two separate teams, two separate codebases, and double the time and money.
What if you could just build one app that works seamlessly on both?
Enter React Native.
You’ve probably heard of it. It’s the Facebook-born framework that lets you build mobile apps using JavaScript and React. But can this web-tech powerhouse really handle the real-time, hardware-hugging world of IoT?
Spoiler alert: Heck yes, it can. And in this deep dive, we’re going to break down exactly how, why, and when you should use React Native for your next IoT project.
First, Let's Get Our Heads Around IoT (It's More Than Smart Fridges)
In simple terms, IoT is a fancy name for a network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other tech to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
These "things" can be:
Consumer Gadgets: Smart speakers (Amazon Echo, Google Home), wearables (Fitbit, Apple Watch), smart thermostats (Nest), and connected lights (Philips Hue).
Industrial Machines: Sensors in a manufacturing plant, GPS trackers on shipping containers, or health monitors on critical infrastructure.
At its core, an IoT system has three main parts:
The Device: The physical "thing" with its sensors and hardware.
The Gateway/Cloud: The middleman that collects, processes, and stores the data (often in the cloud).
The User Interface (UI): The app on your phone or the dashboard on your computer that lets you see the data and send commands back to the device.
This is where React Native shines—it’s a superstar at building that User Interface.
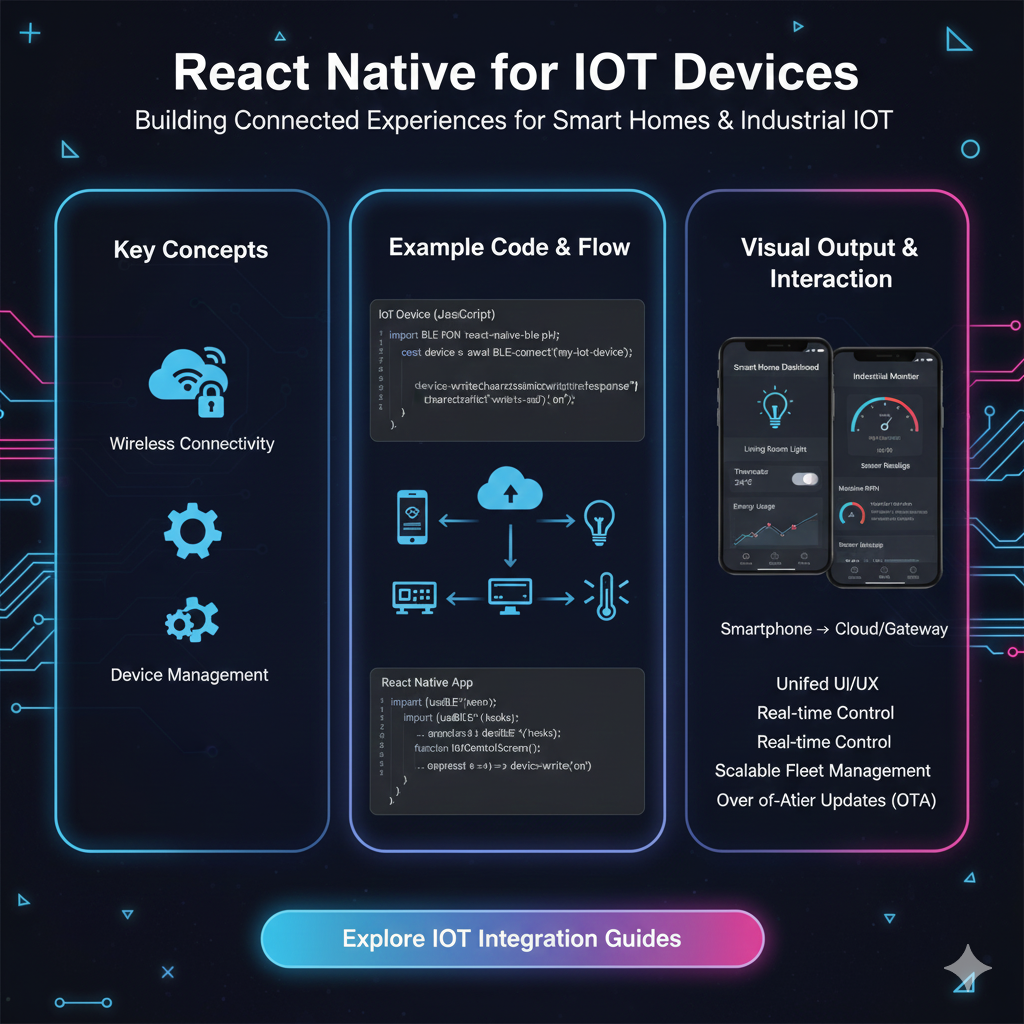
How Does React Native Even Talk to an IoT Device?
Think of it like a conversation. Your React Native app (on your phone) doesn't usually talk directly to the IoT device (like your smart plug). They communicate through a mutual friend: The Cloud.
Here’s the typical flow:
The App Sends a Command: You tap "Turn On" in your beautifully crafted React Native app.
API Call to Cloud: The app sends an HTTP request (like a digital note) to a cloud server via an API. (e.g., "Hey cloud, tell SmartPlug-42 to turn on").
Cloud Talks to Device: The cloud server, which is always listening, receives this note and relays the command to the actual IoT device using protocols like MQTT or WebSockets, which are perfect for real-time, low-power communication.
Device Executes: The smart plug receives the command and turns on.
Confirmation: The plug sends a "success" message back to the cloud, which then updates your React Native app. The UI instantly changes, maybe the button goes from "Turn On" to "Turn Off," and you feel like a wizard.
But what about connecting directly? Sometimes, for things like configuring a new device or for local control without the internet, the app needs to talk directly to the device via Bluetooth (BLE - Bluetooth Low Energy) or Wi-Fi. This is totally possible with React Native thanks to a vibrant ecosystem of community-developed libraries.
Libraries are your best friend here:
For HTTP API Calls: The built-in
fetchor libraries likeaxiosare your go-to.For Real-Time Data (WebSockets): The native
WebSocketobject or libraries likesocket.io-client.For Bluetooth LE: Excellent libraries like
react-native-ble-plxprovide powerful APIs to scan, connect, and communicate with BLE devices.For MQTT: You can use
react-native-mqttto have your app subscribe to MQTT topics directly.
Real-World Use Cases: Where React Native + IoT Gets Real
This isn't just theoretical. Companies are using this combo right now to build incredible products.
Smart Home Management Apps: Imagine one app to rule them all—controlling your lights, thermostat, security cameras, and door locks. A single React Native codebase can provide a consistent UI for both iOS and Android users, saving development costs significantly.
Health and Fitness Wearables: A React Native app can connect via BLE to a fitness band, display real-time heart rate and step counts, and sync historical data to the cloud. The cross-platform nature is key here, as you want to support all your customers, regardless of their phone.
Industrial Monitoring Dashboards: Field technicians can use tablets (both iPads and Android) running the same React Native app to monitor sensor data from industrial equipment, receive alerts, and perform diagnostics.
Retail and Logistics: Apps for warehouse workers that scan BLE beacons on inventory or track assets in real-time can be built efficiently with React Native.
The Good, The Bad, and The Nerdy: Pros and Cons
Let's not sugarcoat it. React Native isn't a magic bullet for every single scenario.
👍 The Pros (Why You Should Consider It):
Code Reusability & Faster Development: This is the big one. Write once, run on both iOS and Android. This cuts development time and cost almost in half.
Hot Reloading for Rapid Iteration: See your changes instantly. This is a game-changer for tweaking the UI of your device controls.
Massive Community & Ecosystem: Stuck on a Bluetooth issue? Chances are, someone has already solved it. The wealth of libraries and community support is immense.
JavaScript Everywhere: If your team already knows JavaScript for web development, the learning curve is much smoother than picking up Swift and Kotlin simultaneously.
Performance is "Good Enough": For most IoT control panels and dashboards, which are not graphics-intensive games, React Native's performance is perfectly adequate.
👎 The Cons (The Reality Check):
The "Bridge" Bottleneck: React Native communicates with native phone modules (like Bluetooth) through a "bridge." For super low-latency, millisecond-critical operations (think: real-time audio processing), this bridge can introduce a tiny delay that might be unacceptable.
Native Module Dependence: For very specific or cutting-edge hardware features, you might need to write your own native modules (in Swift/Objective-C or Java/Kotlin). This requires native knowledge and can break the "write once" promise.
Debugging Can Be Tricky: Sometimes, you're debugging JavaScript, sometimes the native side, and sometimes the bridge in between. It can feel like you have three problems instead of one.
Battery Consumption: If your app is constantly polling for data via BLE or WebSockets, it can be a drain on the phone's battery. Efficient coding is crucial.
Best Practices for Building Rock-Solid React Native IoT Apps
Plan Your Communication Protocol: Decide early on: Will you use mostly Cloud APIs, direct BLE, or a hybrid approach? This architectural decision is foundational.
Embrace State Management: Use state management libraries like Redux Toolkit or Zustand to handle the complex state of your IoT devices (connected/disconnected, loading, error, data values). Your UI should be a reflection of this state.
Handle Errors Gracefully: IoT is messy. Networks fail, Bluetooth disconnects, devices run out of battery. Your app shouldn't crash. It should show helpful messages like "Trying to reconnect..." or "Device not found."
Optimize for Real-Time Updates: Use WebSockets or MQTT for features that need instant feedback (e.g., a live sensor graph) instead of constantly polling the API with HTTP requests.
Security is NOT an Afterthought: Always use HTTPS for your API calls. For BLE, ensure your device uses secure pairing and encrypted characteristics. Never send passwords or sensitive data in plain text.
FAQs: Your Burning Questions, Answered
Q: Can React Native control any IoT device?
A: Mostly, yes. If the device can be controlled via a cloud API or connected via Bluetooth/Wi-Fi that the phone can access, then React Native can be the UI for it.
Q: Is Flutter a better choice for IoT?
A: Flutter is a strong competitor. It compiles to truly native code, which can mean better performance. The choice often comes down to your team's expertise (Dart for Flutter vs. JavaScript for React Native) and specific library support for your hardware.
Q: What's the biggest challenge in using React Native for IoT?
A: Handling the inherent unpredictability of hardware connections. Managing Bluetooth state, reconnection logic, and ensuring a smooth user experience even when things go wrong is the toughest part.
Q: Do I need to learn native development (Swift/Kotlin)?
A: For most projects, no. But for advanced, custom hardware integrations, having that knowledge in your back pocket is a huge advantage. It allows you to write your own native modules when needed.
Conclusion: The Future is Connected (and Cross-Platform)
React Native presents a compelling, cost-effective, and powerful solution for building the mobile face of the Internet of Things. It democratizes IoT app development, allowing smaller teams and startups to compete with giants by building high-quality, cross-platform applications faster.
While it has its limitations for ultra-high-performance scenarios, it hits the sweet spot for the vast majority of consumer and industrial IoT applications. The ability to manage your smart world from a single, consistent app is no longer a luxury—it's an expectation. React Native helps you meet that expectation without breaking the bank.
The fusion of software and hardware is where the most exciting innovations are happening. If you're inspired to start building these kinds of applications yourself, you'll need a solid foundation. To learn professional software development courses that cover the full spectrum, from backend APIs with Python Programming to dynamic front-ends and full-stack mastery with Full Stack Development and the MERN Stack, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. We'll give you the tools to not just use technology, but to build the future with it.
So, what will you connect?


















