Firebase Firestore Complete Guide: Build Real-Time Apps Fast
Tired of slow backends? Our complete Firebase Firestore guide explains real-time sync, security rules & best practices with examples. Learn to build faster apps. Master development with CoderCrafter.
Alright, let’s cut through the noise. You’ve heard about Firebase, you’ve seen “Firestore” pop up in every other developer tutorial, and you’re probably wondering: “Is this just another database hype, or is it actually the game-changer everyone says it is?”
Spoiler: It’s a game-changer. Especially if you’re building anything that needs to feel fast, responsive, and alive without you spending months building backend infrastructure.
Think of it like this: Remember the pain of setting up servers, writing endless API endpoints, and managing database connections? Firestore is like someone said, “What if we just… skipped that?” and built a database you can talk to directly from your app. Mind-blowing, right?
Let’s break it down, no fluff, just what you need to know to start building cooler apps, faster.
What Exactly Is Firebase Firestore?
In the simplest terms, Firestore is a flexible, scalable NoSQL cloud database. But that sentence does it zero justice. Let’s translate:
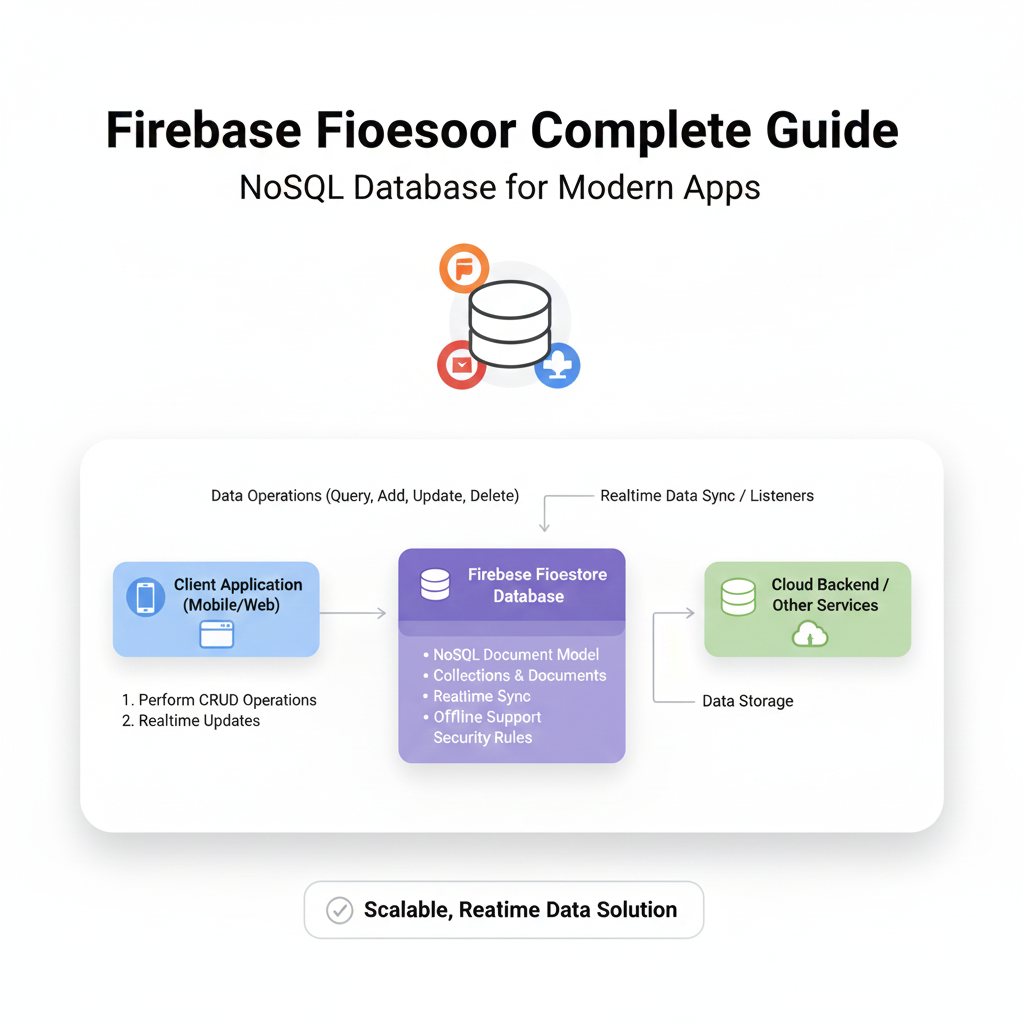
It’s a live, syncing data store for your apps. Unlike a traditional database where you “fetch” data, Firestore lets you listen to data. When the data changes anywhere (on another user’s device, from a server function), it updates everywhere in real-time. Think live chat, collaborative tools, or a dashboard that updates without you hitting refresh—that’s Firestore magic.
Key DNA Traits:
NoSQL: Data is stored in documents (like JSON objects) inside collections. It’s intuitive, like working with JavaScript objects.
Real-time Listeners: The killer feature. Get continuous updates with just a few lines of code.
Offline-First: Your app works even without the internet. It syncs local changes when connectivity is back. User experience? Chef’s kiss.
Serverless-Friendly: Part of the Google Firebase suite, it plays perfectly with Cloud Functions, Auth, and Hosting. You’re building on a full-stack galaxy.
Firestore in the Wild: Real-World Use Cases
This isn’t just theory. Here’s how apps you use (or could build) leverage Firestore:
The Live Collaboration App: Google Docs, Trello, Figma. Multiple users editing the same thing? Firestore’s real-time sync handles the state and updates everyone’s UI instantly.
The Social Feed: A Twitter or Instagram-like feed. New posts? They pop up. New likes? Count updates live. Comments appear without pulling-to-refresh.
The Food Delivery App: Track order status in real-time. “Order Placed” -> “Preparing” -> “On the Way” -> “Delivered”. The driver’s app updates the location, and your map moves. All real-time.
The IoT Dashboard: Connecting sensor data (temperature, humidity) to a live dashboard. Firestore handles the constant stream of updates effortlessly.
Getting Your Hands Dirty: A Practical Example
Let’s say we’re building a simple task manager. Here’s the Firestore mindset.
Structure: You’d have a collection called tasks. Each task is a document inside that collection.
A task document might look like this:
json
{
"id": "auto-generated-id",
"title": "Ship Firestore blog post",
"completed": false,
"createdAt": January 23, 2024 at 12:00:00 PM UTC-5,
"userId": "user_123"
}Code Snippet (Web - JavaScript SDK):
javascript
import { getFirestore, collection, addDoc, onSnapshot } from "firebase/firestore";
// Initialize
const db = getFirestore(app);
// Add a task (Create)
const newTask = {
title: "Learn Firestore deeply",
completed: false,
createdAt: new Date(),
userId: currentUser.uid
};
const docRef = await addDoc(collection(db, "tasks"), newTask);
console.log("Task written with ID: ", docRef.id);
// Listen to ALL tasks in real-time (Read + Real-time)
const unsubscribe = onSnapshot(collection(db, "tasks"), (querySnapshot) => {
const tasks = [];
querySnapshot.forEach((doc) => {
tasks.push({ id: doc.id, ...doc.data() });
});
console.log("Current tasks: ", tasks); // This runs every time data changes
});
// Update a task
await updateDoc(doc(db, "tasks", "specific-doc-id"), {
completed: true
});
// To stop listening later
// unsubscribe();See? No complex server code. You’re directly reading and writing, and onSnapshot is your live wire to the data.
Leveling Up: Best Practices You Can’t Ignore
Structure Data for Your App’s Needs: Denormalize. In NoSQL, it’s okay to duplicate data for faster reads. A user’s name might live in both the
userscollection and repeated in apostscollection to avoid a chain of fetches.Security Rules Are NON-NEGOTIABLE: This is your backend firewall. Never leave your database open. Write strict rules that validate user authentication and data structure.
javascript
// Example rule: Users can only manage their own tasks match /tasks/{taskId} { allow read, write: if request.auth != null && request.auth.uid == resource.data.userId; }Index Your Queries: Firestore will yell at you if you run a compound query without an index. It even gives you a link to create one. Click it.
Cost Awareness: You pay per read, write, and delete. Design efficient data structures, use pagination (
limit,startAfter) for large lists, and avoid deeply nested listeners you don’t need.Emulate Locally: Use the Firebase Emulator Suite. It lets you develop and test Security Rules and Cloud Functions offline. It’s a lifesaver.
FAQ: The Stuff You’re Actually Searching For
Q: Firestore vs. Realtime Database (RTDB). Which one?
A: RTDB is one giant JSON tree. Great for very simple, low-latency things (like presence systems). Firestore is the newer, more powerful sibling. Better queries, structured data, generally the go-to for 99% of new projects.
Q: Is it really “serverless”? What about complex logic?
A: Yes, but you’ll often pair it with Cloud Functions (server-side code that runs in response to events). Example: When a new user document is created, a Function can send a welcome email. This is where the magic of a full-backend truly unfolds.
Q: How do I handle relations between data?
A: You can use references (docRef) to point to documents in other collections. You’ll fetch that data in a second step. For complex relational needs, a SQL database might be better, but Firestore references handle most cases well.
Q: Can it scale? Like, for real?
A: It’s backed by Google Cloud. It scales automatically. Your job is to model your data and queries efficiently.
Conclusion: Why This Matters for You
Firestore fundamentally changes the development speed. It allows small teams and solo developers to build production-grade, real-time applications that were previously the domain of large engineering teams. It’s not just a tool; it’s a force multiplier.
The learning curve? Surprisingly gentle. The payoff? Massive.
Mastering tools like Firestore is what separates hobbyist coders from professional developers who can ship robust, scalable applications. It’s about choosing the right tool for the job and building with confidence.
Ready to move beyond the basics and build the architecture of real-world apps? To learn professional software development courses such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and the powerhouse MERN Stack, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. We don’t just teach syntax—we teach you how to think like a developer and build like an engineer.
Firestore is a powerful piece of that puzzle. Start a project. Break things. Set up those security rules. Build something live. That’s how the craft is learned. Now go code.


















