API Caching Guide 2025: Strategies for Blazing-Fast Performance
Tired of slow APIs? Our 2025 guide to API caching breaks down Redis, HTTP caching, and real-world strategies used by giants like RevenueCat to boost speed & cut costs.
Ever been in the middle of a seamless online experience—streaming a show, scrolling through social media, or checking out at an online store—only to have it grind to a halt with a spinning wheel of doom? We’ve all been there. More often than not, that frustrating lag can be traced back to a slow backend API, waiting on a database query or a complex computation.
In today’s digital landscape, speed isn't just a luxury—it's a necessity. A former Amazon engineer once highlighted that every 100 milliseconds of latency can cost 1% in sales. That’s a massive hit for any business.
The good news? There’s a powerful tool in a developer's arsenal to combat this: API caching. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly what caching is, explore real-world strategies that actually work, and show you how to implement it to make your applications lightning-fast.
What Exactly is API Caching, and Why Should You Care?
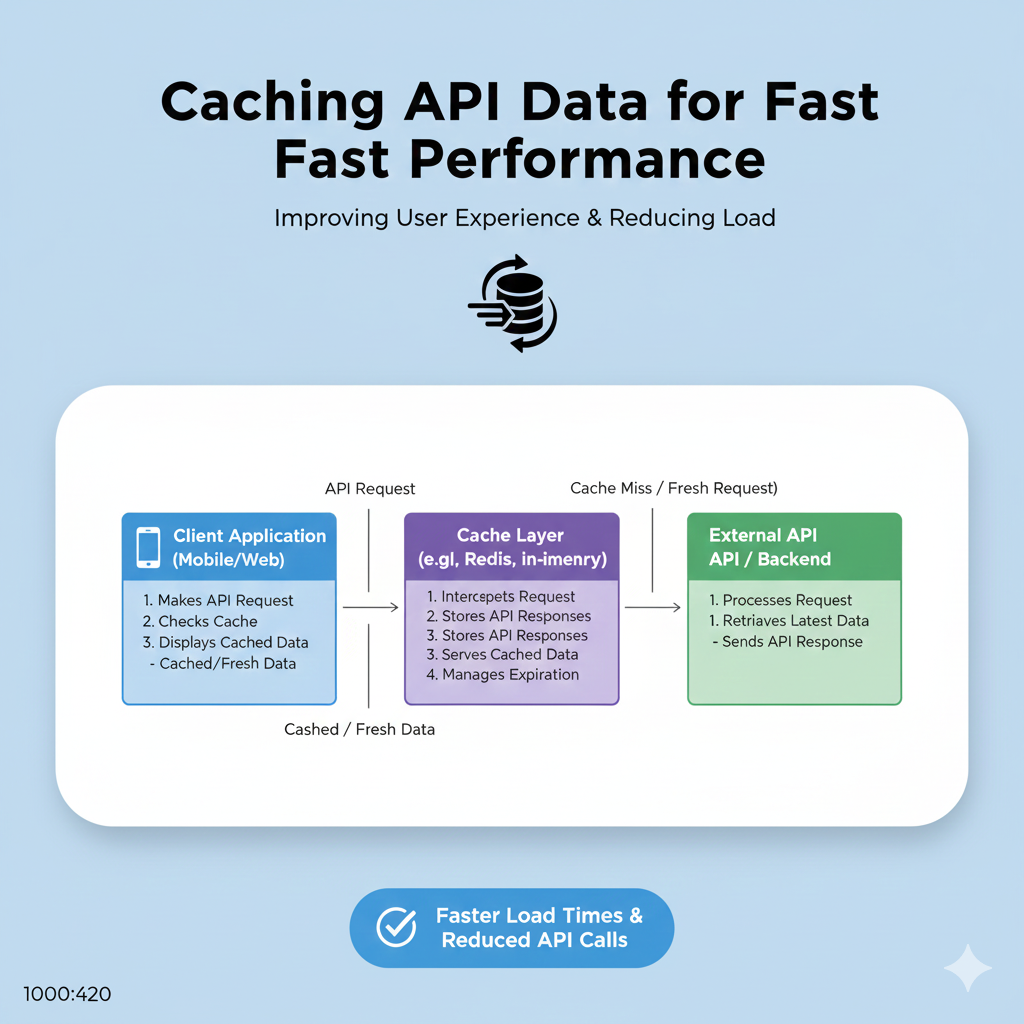
At its core, caching is like having a cheat sheet. Instead of running to the library (your database) to look up the same answer for every single person who asks, you jot it down on a sticky note (your cache) for quick, easy access.
Technically, it’s the process of temporarily storing copies of frequently accessed data in a faster, more accessible storage layer. When your API needs that data again, it grabs it from the cache in microseconds instead of executing a slow database query or a heavy computation.
Here’s the real kicker: the benefits are game-changing:
⚡ Lightning-Fast User Experiences: Near-instant responses keep users happy and engaged.
🛡️ Unshakeable Scalability: Your servers can handle traffic spikes and more concurrent users without breaking a sweat.
💰 Serious Cost Savings: By dramatically reducing database load and computation, you can save on cloud infrastructure costs.
Where Does the Magic Happen? Caching Layers Explained
Caching isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. You can implement it at different points in your data's journey for maximum effect.
Caching Layer | What It Is | Best For | Common Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
Client-Side | Data stored directly in the user's browser or app. | Personalizing repeat visits, offline functionality. | Browser Cache, |
Edge (CDN) | Copies of data stored on servers physically closer to users worldwide. | Delivering static assets and even API responses globally with low latency. | Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, Akamai |
API Gateway | A central entry point that can store responses before requests hit your backend. | Reducing load on core services, request aggregation. | AWS API Gateway, Kong, Apigee |
Server-Side | The heavy lifter, caching data in your application's backend infrastructure. | Accelerating database queries and business logic. | Redis, Memcached, Valkey |
Think of it as a series of defensive lines. A request from a user in Tokyo for a popular product might be fulfilled instantly by a CDN edge server in Japan (Edge Caching). If it's a first-time request, the API Gateway might have a cached response ready. If not, the application checks its fast in-memory cache (Server-Side) before finally, as a last resort, querying the primary database.
Battle-Tested Caching Strategies: Pick Your Weapon
Choosing the right strategy is crucial. Here’s a breakdown of the most effective patterns, explained simply.
For Read-Heavy Workloads
Cache-Aside (Lazy Loading): This is the go-to strategy for most developers. Your app code is in charge. On a request, it checks the cache first. On a miss, it fetches from the database, populates the cache, and then returns the data. It's simple and gives you fine-grained control. Use it for user profiles, product catalogs, or social media posts.
Read-Through Cache: Here, the cache itself is smart. If data is missing, the cache system automatically fetches it from the database, stores it, and returns it. Your application just asks for data; the cache handles the rest. Great for high-traffic systems where you want to abstract away cache management, like a news website caching headlines.
For Write-Heavy or Critical Data
Write-Through Cache: Consistency is key. Data is written to both the cache and the database simultaneously. This ensures the cache is never stale but adds a bit of latency to write operations. Ideal for banking apps where account balance accuracy is critical.
Write-Behind (Write-Back) Cache: Need raw write speed? Data is written to the cache first, and the cache then asynchronously updates the database in batches. This is blazing fast but risks a small data loss if the cache fails before syncing. Perfect for logging high-frequency events, IoT sensor data, or social media activity like likes and comments.
The Secret Weapon: HTTP Caching
Don’t overlook the power built into the HTTP protocol itself! By using headers, you can instruct browsers, apps, and CDNs on how to cache your API responses.
Cache-Control: The boss directive. Usemax-age=3600to tell clients they can reuse the response for an hour without checking back.ETag/If-None-Match: Like a data fingerprint. The server sends anETagwith a response. Later, the client sends thatETagback. If the data hasn’t changed, the server replies with a lightweight304 Not Modifiedstatus, saving bandwidth.
Real Talk: Lessons from the Tech Giants
Theory is great, but let's see how this plays out at scale.
RevenueCat, a platform handling over 1.2 billion API requests daily, openly states it would be impossible without caching. Their genius move? Implementing a multi-pool strategy:
Dedicated Pools: For expensive, rarely-changing data.
Mirrored Pools: For read-heavy workloads to distribute load.
Gutter Pools: A brilliant fallback—if the main cache misses and the database is down, they serve slightly stale data from a "gutter" pool with a low TTL, keeping the app running.
Twitter/X provides a crucial cautionary tale. Caching issues have caused major outages, like cache stampedes (thundering herds of requests overwhelming the database when a popular key expired) and inconsistency between cache layers. The lesson? Caching without robust monitoring and observability is a recipe for disaster.
Your Action Plan: Implementing Caching Without the Headache
Ready to implement? Follow these steps:
Identify Cache Candidates: Start with frequently accessed, rarely changing data. User profiles, product details, and static configuration are perfect. Avoid highly dynamic data like real-time location.
Choose Your Tools: For server-side caching, Redis (or its open-source fork Valkey) is the industry standard for its speed and rich data structures. For simpler needs, Memcached is a lightweight alternative.
Set Smart Expirations (TTL): Use short TTLs (seconds/minutes) for dynamic data and long TTLs (hours/days) for static data. Always pair with a cache eviction policy like LRU (Least Recently Used) to automatically clear old data when the cache is full.
Never Forget Invalidation: This is the "hard part." Have a clear plan for deleting or updating cached data when the source data changes. Use TTL as a safety net, but for important data, implement event-driven invalidation (e.g., publish a message when a product price updates so the cache can clear that key).
Monitor Relentlessly: Track your cache hit ratio (aim for >90%), latency, and eviction rates. Tools like Grafana can help you visualize this and spot problems before they cause outages.
Level Up Your Skills
Mastering concepts like API caching is what separates good developers from great architects. It’s a core pillar of building scalable, resilient, and high-performance systems that users love.
To learn professional software development courses that dive deep into backend architecture, system design, and tools like Redis, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. Whether you're interested in Python Programming, Full Stack Development, or the MERN Stack, you'll gain the hands-on skills needed to build the fast, modern applications that define today's web.


















