Kubernetes in DevOps: Best Practices for Scalable Cloud-Native Applications (2025 Guide) Meta Description

Discover the essential role of Kubernetes in DevOps workflows. Learn best practices, real-world examples, and expert deployment tips to build secure, scalable cloud-native applications. Take your coding skills further with professional courses at codercrafter.in.
Cloud-native applications and DevOps are transforming how businesses deliver value to customers. At the center of this transformation is Kubernetes—the open-source orchestrator powering millions of scalable production environments. If maximizing agility, reliability, and scalability is the goal, Kubernetes is the indispensable tool modern DevOps teams swear by.
To master Kubernetes, you need both theory and hands-on skills. To learn practical software development, Python programming, Full Stack, or MERN Stack from industry experts, visit and enroll at codercrafter.in today.
What Is Kubernetes? A Modern Definition
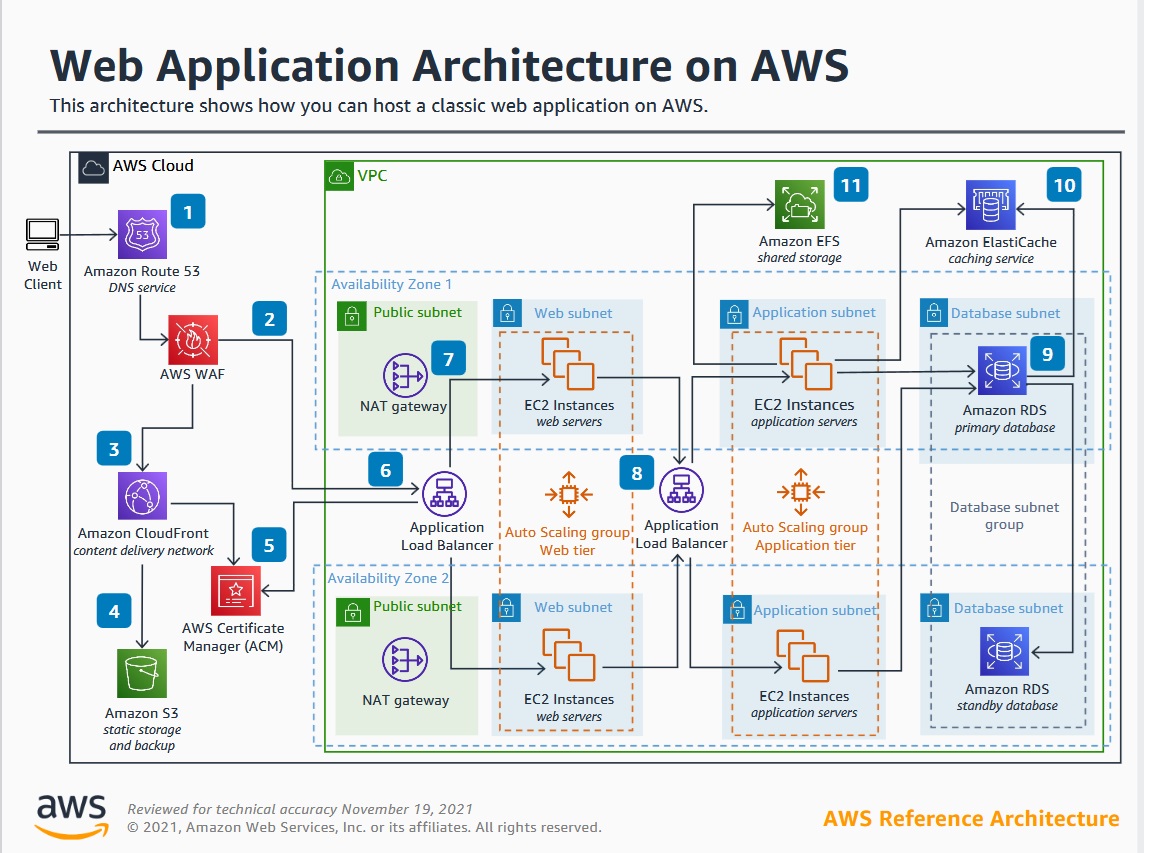
Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Picture Kubernetes as a distributed “cluster manager” that abstracts the underlying infrastructure and enables engineers to run, update, and monitor containers at scale—across data centers, clouds, or hybrid environments.
Key benefits: Automated scaling, rolling updates, high availability, self-healing, resource optimization
Core objects: Pods, Deployments, Services, ReplicaSets, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, Namespaces
Architectural components: Control Plane (API Server, Scheduler, etcd, Controller Manager), Nodes (Worker Machines), Kubelets, and Kube-Proxies
Kubernetes is exceptionally flexible—capable of everything from small dev clusters to global production workloads. It enables DevOps culture by making reliable, automated software delivery a reality.
Why DevOps and Cloud-Native Needs Kubernetes
DevOps is more than tooling—it’s a culture of collaboration, integration, and continuous improvement. Cloud-native applications build upon this foundation by emphasizing microservices, containers, automation, and observability.
Kubernetes became the “operating system” for these new patterns because it:
Manages the lifecycle of containers automatically, so teams can focus on building business logic, not infrastructure plumbing.
Provides deployment consistency so applications behave identically from a developer’s laptop to massive cloud clusters.
Enables advanced DevOps workflows: Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC), Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD), GitOps, and automated rollbacks.
Leading tech companies, fintechs, e-commerce giants, and research institutions rely on Kubernetes to power everything from AI workloads to global customer-facing platforms.
Real-World Use Cases: Kubernetes in Action
Kubernetes isn’t just theoretical. Here’s how it’s transforming industries:
1. Finance & AI
Bloomberg: Powers 14,000+ Terminal applications, achieving up to 95% hardware utilization.
OpenAI: Runs massive distributed AI training jobs across GPU clusters using Kubernetes for scalable, reliable orchestration.
2. E-commerce & Retail
JD.com: Handled $23 billion in transactions over an 11-day sale with Kubernetes, slashing deployment times and IT costs by up to 30%.
Shopify: Migrated to Kubernetes to seamlessly auto-scale during Black Friday surges.
3. Media & Entertainment
New York Times: Reduced app deployment times from 45 minutes to seconds.
Spotify: Runs hundreds of microservices, improving release agility and uptime.
Tinder: Orchestrates 15,000+ pods, ensuring smooth, high-volume operations.
4. Healthcare & Research
CERN: Manages scientific workloads with Kubernetes, reducing infrastructure overhead.
Healthcare Platforms: Achieve strict compliance and data portability.
More Inspiring Examples
Telecom: Nokia uses Kubernetes for scalable, cloud-agnostic network functions.
Startups & SMBs: Airbnb, Adidas, and others deploy quickly and scale effortlessly, thanks to Kubernetes.
Want to build the skills to deploy at this scale? Explore in-demand Kubernetes skills at codercrafter.in.
Kubernetes in DevOps: Best Practices for Scalable Success
Kubernetes is powerful—but its complexity can backfire without careful design. Implementing these field-tested best practices will help teams build resilient, secure, and cost-effective cloud-native systems.
1. Organize with Namespaces
Use namespaces to logically divide resources (e.g., dev, staging, prod) for safety and clarity.
Apply resource quotas for each namespace to prevent noisy neighbors and enforce isolation.
Consistently label namespaces (owner, project, purpose) for easier tracking and automation.
2. Automate Health Checks
Configure readiness and liveness probes for all services to enable intelligent traffic routing and automatic self-healing (restarts, rollbacks) during failures.
Design probes to only permit ready, healthy pods to receive traffic.
3. Leverage Autoscaling
Employ Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) for CPU/memory-driven scaling, Vertical Pod Autoscaler for right-sizing, and Cluster Autoscaler for dynamic infrastructure.
Use Persistent Volumes (PVs) to support stateless pods and enable seamless scaling.
4. Control Resources and Scheduling
Set resource requests and limits for CPU, memory, and storage per pod.
Apply taints/tolerations and affinity/anti-affinity to control workload placement—ensuring best use of specialized hardware and promoting high availability.
5. Secure by Design
Mandate Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to enforce the principle of least privilege and prevent unauthorized activities.
Monitor and restrict internal communications with network policies and external access via firewalls.
Store secrets securely using external solutions (e.g., HashiCorp Vault, AWS/GCP managers).
6. Optimize CI/CD Workflows
Host your CI/CD tooling in Kubernetes for uniform workflows.
Adopt Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and GitOps: all configs in git, automated, auditable, and easy to roll back.
7. Choose Declarative, Versioned Configurations
Use YAML/JSON config files treated as code (ideally in Git) for repeatability and documentation.
Incorporate review gates and change approvals in workflows.
8. Manage Deployments Intelligently
Employ advanced deployment strategies: Blue-Green, Canary, Rolling Update, and Recreate as fits your risk profile and downtime tolerance.
9. Monitor, Log, and Audit Everything
Integrate with observability stacks (Prometheus for metrics, Grafana for dashboards, ELK/Fluentd for logs, OpenTracing for distributed traces).
Enable audit logs for Kubernetes API activity and enforce log retention.
10. Continuously Update and Upgrade
Regularly upgrade Kubernetes, control plane, and cluster components to benefit from security patches, performance improvements, and new features.
Test upgrades in staging before production rollouts.
11. Reduce Image Size and Attack Surface
Use minimal OS images (e.g., Alpine Linux).
Remove unnecessary packages and regularly scan for vulnerabilities.
12. Automate Policy Enforcement at Scale
Use admission controllers (OPA, Kyverno) for compliance, security, and resource policies.
13. Optimize Storage Solutions
Design storage for persistent workloads—choose appropriate PV, PVC, and StorageClass options for the use case.
14. Plan for High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Always run multiple replicas and spread them across zones and failure domains using topology spread constraints.
Build these practices into your learning with hands-on projects at codercrafter.in.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What are the steps for deploying in Kubernetes?
Set up a Kubernetes cluster (cloud, on-prem, or local like Minikube).
Containerize the application and push the image to a registry.
Write manifests (YAML) for deployment, service, config, etc.
Deploy using
kubectl apply -f file.yaml.Expose via Service/Ingress and verify pods.
Monitor health and logs using preferred observability tools.
Q2. How many types of deployments exist in Kubernetes?
Rolling Update (gradual replacement)
Recreate (stop old, start new)
Blue-Green (switch to new version once ready)
Canary (roll out to small subset before full deployment)
A/B testing (split traffic based on conditions).
Q3. How can Kubernetes deployments be scaled efficiently?
Scale with:
Manual scaling:
kubectl scale deployment my-deploy --replicas=5Dynamic: Set up Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) for CPU/memory or custom metric-based scaling.
Q4. What is a Helm Chart?
A Helm chart is a package of pre-configured Kubernetes resources, acting as a package manager for installation, upgrades, and consistent deployments across environments.
Q5. Is Kubernetes secure?
Kubernetes itself offers extensive security features but must be configured and managed properly—use RBAC, audit logs, encrypted Secrets, external Secrets Managers, and scan images regularly.
Real-World Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Steep learning curve, misconfigured clusters, and insecure defaults.
Solution: Invest in continuous DevOps education (like courses at codercrafter.in), adopt tested IaC templates, automate policy enforcement, and integrate robust monitoring.
Challenge: Scaling and cost spikes during unpredictable traffic surges.
Solution: Dynamic autoscaling, resource quotas, and careful monitoring help optimize spend and performance.
Challenge: Outage risks during updates.
Solution: Rolling updates, readiness/liveness probes, Pod Disruption Budgets, and canary releases dramatically reduce downtime and risk.
Conclusion: The Future Is Kubernetes
Kubernetes has become the foundation for scalable, reliable, and efficient cloud-native applications. By following the best practices and real-world strategies outlined here, teams unlock performance and innovation across any industry.
Whether building the next Spotify, revolutionizing healthcare, or simply modernizing operations, Kubernetes sets the technical standard for DevOps. But as with any powerful tool, successful adoption requires results-focused learning and a solid grasp of engineering fundamentals.
Take the next step toward Kubernetes mastery with hands-on courses in Python, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack—available now at codercrafter.in. Future-proof your career with world-class instruction and community support.
Ready to become a DevOps and Kubernetes expert? Start your learning journey at codercrafter.in and join a community of innovators building tomorrow’s cloud-native solutions.