What is Computer Hardware? Definition, Components, and Examples
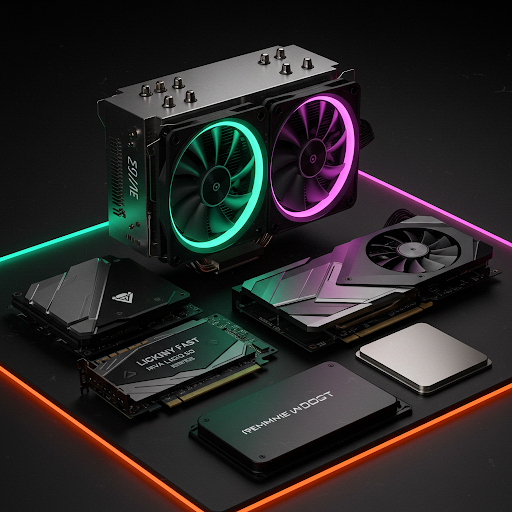

Learn about computer hardware, its definition, essential components like CPU, RAM, motherboard, and storage devices, and their roles in a computer system.
Introduction
Computer hardware refers to the physical components that make up a computer system. Unlike software, which consists of programs and operating systems, hardware includes all the tangible parts of a computer. These components work together to process, store, and manage data efficiently.
Key Components of Computer Hardware
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Often called the "brain" of the computer, the CPU is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
Popular CPU brands: Intel and AMD.
Motherboard
The main circuit board that connects and facilitates communication between all hardware components.
Contains essential slots for RAM, CPU, GPU, and storage.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Short-term memory that stores data currently in use.
Higher RAM capacity improves multitasking and overall speed.
Storage Devices
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) – Traditional, slower, mechanical storage.
SSD (Solid State Drive) – Faster, modern storage for improved performance.
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Converts electricity from an outlet into a usable form for the computer.
Different wattages support various hardware configurations.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Handles image rendering, gaming, and video processing.
Two main types: Integrated (built into CPU) and Dedicated (separate GPU like NVIDIA or AMD Radeon).
Input and Output Devices
Input Devices: Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone, Scanner.
Output Devices: Monitor, Printer, Speakers.
How Hardware and Software Work Together
While hardware provides the structure and physical functions of a computer, software (such as operating systems and applications) tells the hardware what to do. Without hardware, software cannot operate, and vice versa.
Conclusion
Computer hardware is the foundation of any computing device. Whether it’s a desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone, all computers rely on hardware to function effectively. Understanding these components helps users upgrade, troubleshoot, and optimize their systems for better performance.