OTP Authentication Explained: How One-Time Passwords Secure Your Logins
What is OTP authentication? Discover how one-time passwords work, their real-world use cases, and best practices to keep your accounts safe. Learn key differences between HOTP and TOTP.
We've all been there. You type in your password, and then bam—your phone buzzes with a random six-digit code. You copy it, paste it, and you're in. That quick, sometimes slightly annoying, extra step is called OTP Authentication, or One-Time Password authentication.
It's one of those behind-the-scenes tech heroes that's quietly become the backbone of our online security. In a world where data breaches are common and passwords alone just don't cut it anymore, OTPs are the trusted bouncer that double-checks your ID before letting you into the party.
But what exactly is it, and why is it so important? Let's peel back the layers.
What is OTP Authentication, Really?
At its core, OTP authentication is a security method that adds a second layer of identity verification. After you enter your username and password (the first factor), the system sends you a unique, temporary code that's valid for only one login session or transaction and expires after a short time.
Think of your password as a key to your house. An OTP is like a security guard who checks that key and then asks for a secret handshake that changes every single time. Even if someone steals your key (password), they can't get past the guard without that specific, time-sensitive handshake.
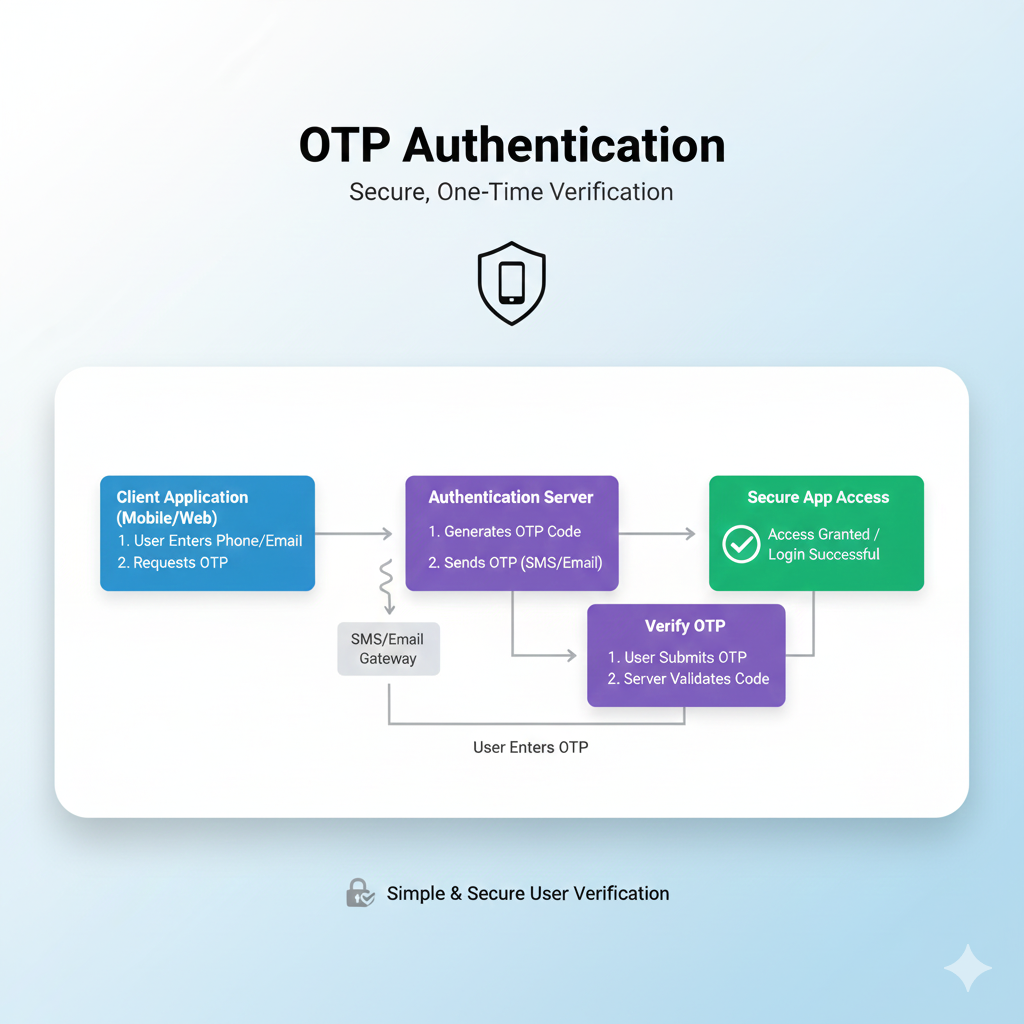
How Does an OTP Actually Work? The 5-Step Flow
The process is elegantly simple and happens in seconds:
You Log In: You enter your regular username and password on a website or app.
The System Triggers an OTP: If your credentials are correct, the system's authentication server generates a unique OTP.
The Code is Sent: This code is delivered to you via a pre-registered channel. This is most commonly an SMS to your phone, but it can also be an email, a voice call, or it can be generated directly within an authenticator app like Google Authenticator.
You Enter the Code: You receive the code and enter it into the prompt on the website or app.
Access is Granted (or Denied): The system verifies that the code you entered matches the one it generated, checks that it hasn't expired, and then grants you access. If the code is wrong or too old, you're staying out.
HOTP vs. TOTP: What's the Difference?
Not all OTPs are created equal. The two main algorithms are HOTP and TOTP, and understanding the difference is key.
Feature | HOTP (Hash-Based OTP) | TOTP (Time-Based OTP) |
|---|---|---|
Based On | A counter (event-based). | The current time. |
How it Changes | Changes each time you request a new code (e.g., press a button on a fob). | Changes automatically at fixed intervals (e.g., every 30 seconds). |
Validity Period | Valid until used. | Typically valid for 30-60 seconds. |
Best For | Offline environments or situations where time sync is difficult. | Most online applications (banks, email, social media). |
Common Example | Physical security fobs. | Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator apps. |
In short: TOTP (time-based) is more common and generally considered more secure for everyday online use because the window for misuse is so tiny. HOTP (counter-based) is great for offline tools but is more vulnerable to replay attacks if a code is intercepted and used before you are.
Real-World Use Cases: Where Do You See OTPs?
OTPs aren't just for big banks anymore. You encounter them daily:
Logging into Sensitive Accounts: Your email, social media, or cloud storage when from a new device.
Online Banking & Financial Transactions: Authorizing a login or confirming a money transfer.
E-commerce Checkouts: Adding an extra layer of security to your final purchase.
Account Recovery: Proving your identity to reset a forgotten password.
New User Registration: Verifying a phone number or email address when you sign up for a new service.
Workplace Access: Securing access to company networks, VPNs, and internal systems, especially in a Zero-Trust security model where no one is trusted by default.
Best Practices for Using OTPs (For Users & Businesses)
For this system to work well, both sides have a role to play.
For Users:
Prefer Authenticator Apps: When given a choice, opt for an app (like Authy or Google Authenticator) over SMS. Apps generate codes locally on your device, making them less susceptible to interception than SMS.
Secure Your Recovery Channels: The phone number or email used for OTPs is a major target. Protect them with strong passwords and, ideally, their own 2FA.
Never Share the Code: Legitimate companies will never call, email, or text you asking for your OTP. It's always a scam.
Act Fast: Codes expire quickly. If you request one, be ready to use it.
For Businesses/Developers Implementing OTPs:
Set Sensible Expiry Times: Codes should expire quickly (2-10 minutes) to limit the attack window, but not so fast that they frustrate users.
Implement Rate Limiting: Block attackers from making thousands of guesses by limiting how many OTP attempts are allowed per user/IP address.
Have a Fallback Channel: If SMS fails, allow the code to be sent via email or voice call as a backup.
Keep Messages Clear: The SMS or email should clearly state the code, the company name, and its purpose (e.g., "Your CoderCrafter login code is: 456789").
Consider Passwordless Flows: OTPs can be used for passwordless authentication, where the code itself is the primary credential, eliminating password-related risks entirely.
Choose a Reliable Provider: If sending SMS OTPs, partner with a provider that guarantees high deliverability rates and speed, as delays can break the user experience.
💡 Building Secure Systems? Understanding the architecture of secure authentication is crucial for modern developers. To learn professional software development courses that cover backend security, API design, and full-stack implementation—such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack—visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is SMS-based OTP secure?
A: It's more secure than just a password, but it's the weakest OTP method. SIM-swapping attacks or interception of SMS messages can compromise it. Authenticator apps or hardware tokens are more secure choices.
Q: What if I don't receive the OTP SMS?
A: First, check for signal issues. Then, use the "Resend Code" option. Most systems offer a backup method, like sending the code via email or an automated voice call. If all else fails, contact customer support.
Q: Can OTPs be hacked?
A: While robust, no system is 100% foolproof. The main risks are phishing (tricking you into giving up the code), SIM-swap fraud (for SMS), or malware on your device. Using authenticator apps significantly reduces these risks.
Q: What's the "secret key" in an authenticator app?
A: When you set up an app, you scan a QR code. That code contains a "secret key"—a unique seed value stored on both your device and the server. This key, combined with the current time, generates the same TOTP code on both ends without needing to transmit it.
Conclusion
OTP authentication has evolved from a niche security tool into an essential part of our digital fabric. It represents a practical balance between robust security and user convenience, effectively combating the massive threat of password reuse and theft.
As we move towards a future with more passwordless and biometric authentication, the principles behind OTPs—dynamic, time-bound verification—will continue to be relevant. For now, the next time you sigh at that extra step, remember: those six digits are a small price to pay for keeping your digital life locked down tight.
The key to leveraging technology like OTP is a deep understanding of how it works under the hood. For aspiring developers and engineers looking to build secure, modern applications, mastering these concepts is fundamental. To learn professional software development courses that dive deep into authentication, security protocols, and full-stack engineering—such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack—visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in.


















