React Native
Build a Full Mobile App Backend: Appwrite + React Native Guide (2025)
12/8/2025
5 min read
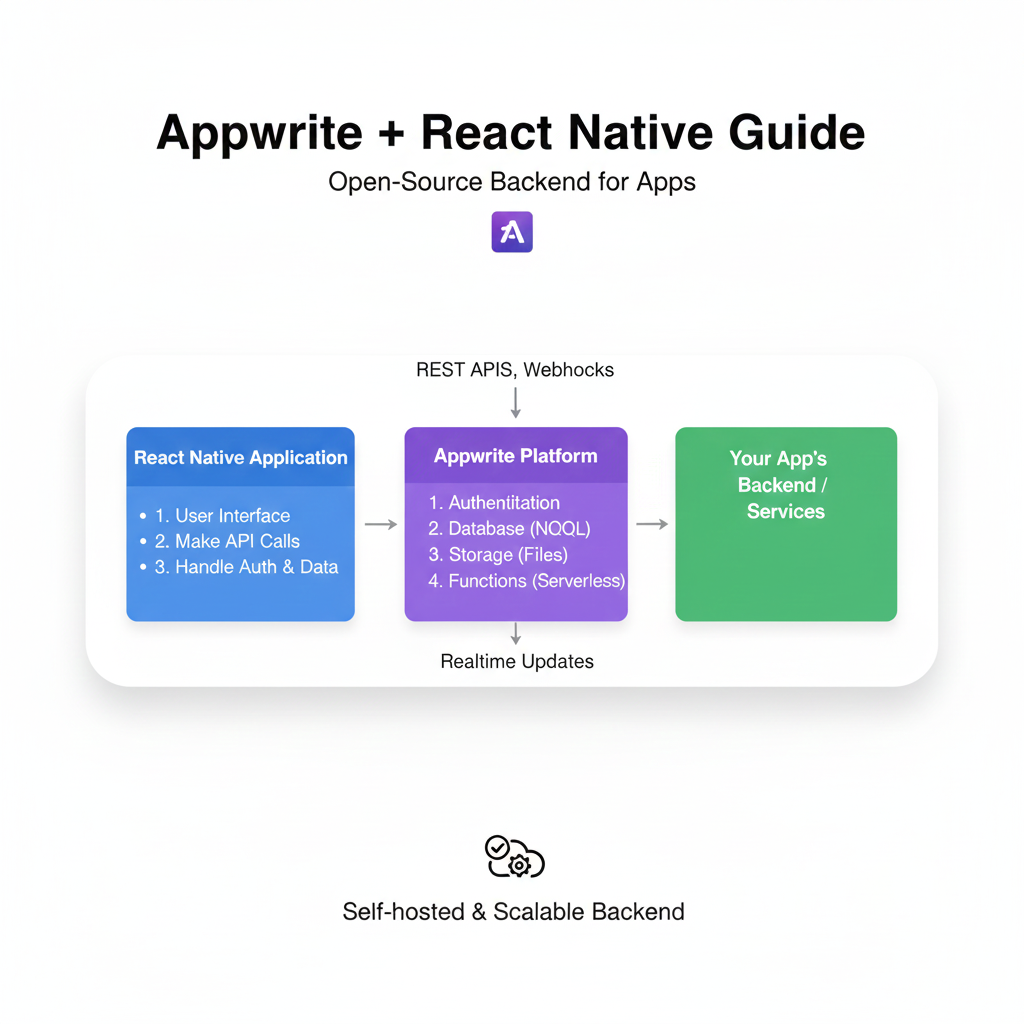
Step-by-step guide to integrating Appwrite with React Native. Learn authentication, databases, storage, and real-time features with code examples. Build pro mobile apps faster.









