GraphQL in React Native: The Complete 2025 Guide for Developers

Struggling with REST API limitations in your React Native apps? Learn how to integrate GraphQL for faster, flexible data fetching. Includes setup, code examples, best practices & FAQs. Level up your skills with CoderCrafter's professional courses
GraphQL in React Native: The Complete 2025 Guide for Developers
Taming the Data Beast: Your Ultimate Guide to Using GraphQL in React Native
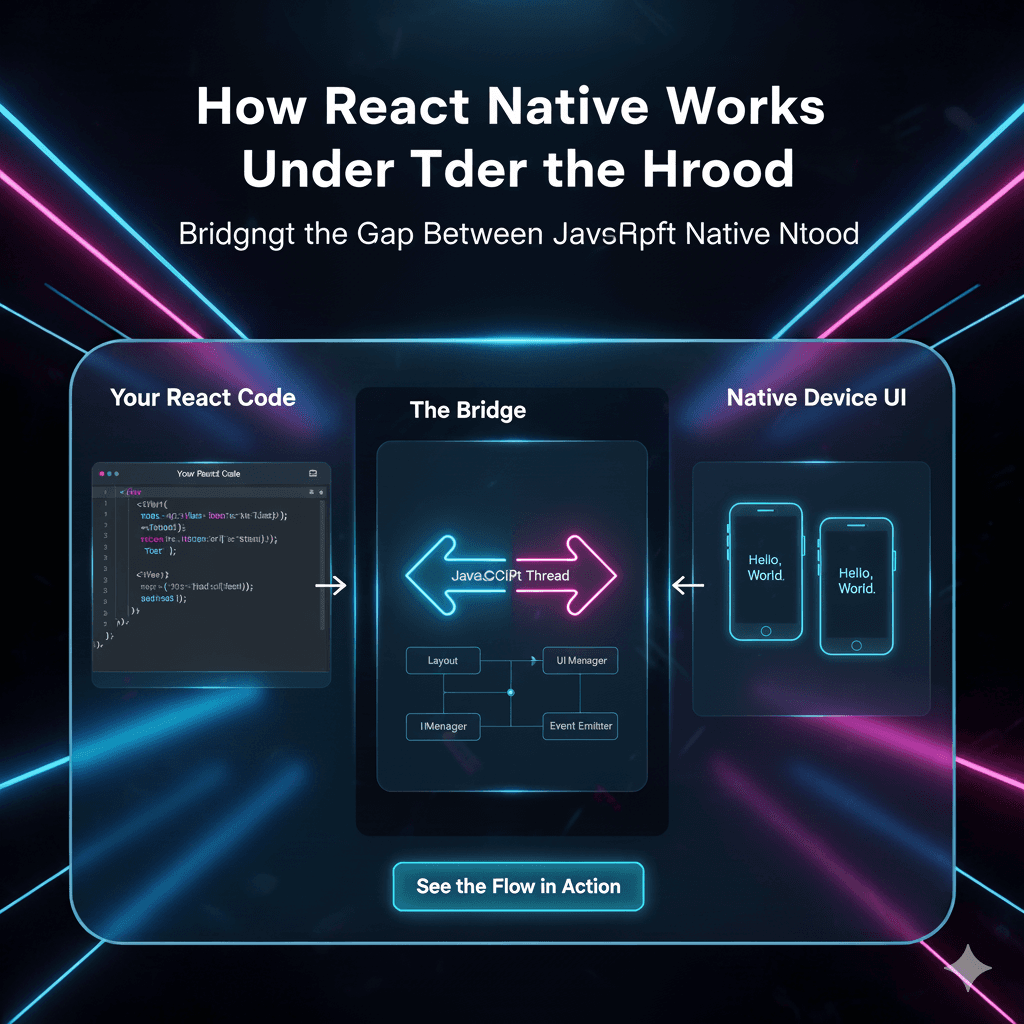
Let’s be real for a second. Building a slick, fast React Native app is an amazing feeling. But then you hook it up to a REST API, and suddenly, you’re drowning in a sea of endpoints. Need a user’s name and profile pic? That’s one call. Need their recent posts? That’s another. Oh, you also need the comments on those posts? Grab the popcorn, we’re going on a waterfall fetching adventure.
Sound familiar? You’re not alone. This over-fetching (and under-fetching) of data is why many developers are making the switch to GraphQL. And if you’re building with React Native, this combo is like giving your app a supercharged engine.
So, grab your favorite drink, and let’s break down exactly what GraphQL is, why it’s a game-changer for mobile, and how you can implement it in your React Native projects today. No fluff, just the good stuff.
What Exactly is GraphQL? (Spoiler: It’s Not a Database)
First things first, let’s clear the air. GraphQL is a query language for your API. It’s not a database, a framework, or a replacement for SQL. Think of it as the intelligent middleman between your frontend (your React Native app) and your backend.
Created by Facebook in 2012 (and open-sourced in 2015), GraphQL’s core idea is simple: Ask for exactly what you need, get exactly that. Instead of the server deciding what data comes back from a fixed endpoint (like /api/users/123), the client sends a detailed “shopping list” of data requirements.
The Key Mental Shift:
REST: You call a location (an endpoint) to get a fixed set of data. "Go to the ‘user cabinet’ and bring me whatever’s inside."
GraphQL: You send a description of the data you need to a single endpoint. "I need the user’s name, their last 3 post titles, and the first comment on each post."
This shift is especially powerful for mobile applications like those built with React Native, where network efficiency, data usage, and speed are critical for user experience.
Why GraphQL is a React Native Developer’s Best Friend
No More Over-fetching: Remember getting a massive JSON blob from a user endpoint when you only needed a
username? GraphQL eliminates that. Your query defines the fields, so the response is lean.No More Under-fetching (a.k.a. The Waterfall): Need data from related resources (user + posts + comments)? With REST, that’s multiple round trips. With GraphQL, you can get it all in one single, declarative query.
Strongly Typed & Self-Documenting: The GraphQL schema acts as a contract between frontend and backend and as built-in documentation. Tools like GraphiQL or Apollo Studio let you explore the API visually—a huge developer experience win.
Frontend Empowerment: UI changes often require different data. With GraphQL, frontend developers can specify new data needs without waiting for backend teams to create new endpoints. It fosters faster iteration.
Getting Your Hands Dirty: Setting Up GraphQL in React Native
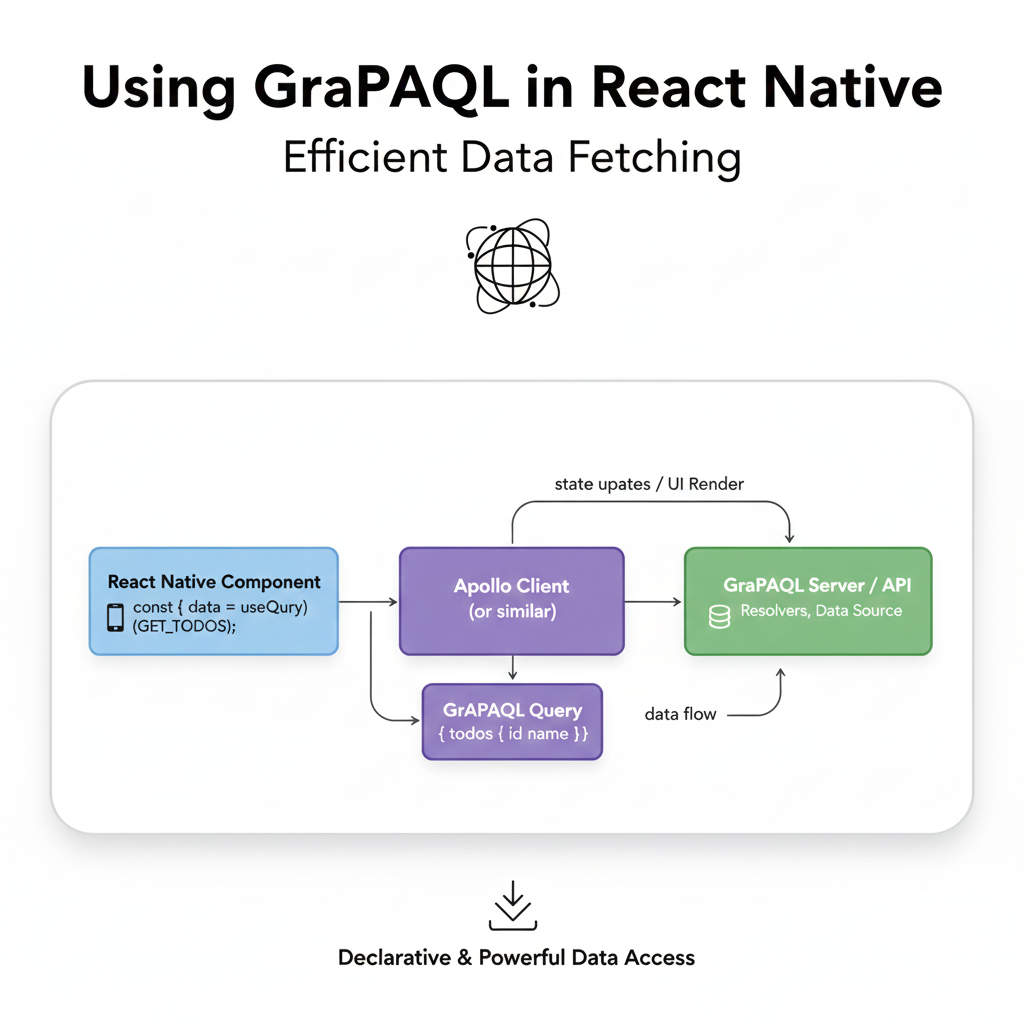
Enough theory. Let’s see how this works in practice. We’ll use the most popular client library: Apollo Client. It handles caching, state management, and the nitty-gritty of network requests beautifully.
Step 1: Set Up Your React Native Project
bash
npx react-native init MyGraphQLApp
cd MyGraphQLAppStep 2: Install Apollo Client Dependencies
bash
npm install @apollo/client graphqlStep 3: Configure the Apollo Client
You typically set this up at the root of your app, wrapping your component tree in an ApolloProvider.
javascript
// App.js
import React from 'react';
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache, ApolloProvider, createHttpLink } from '@apollo/client';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
import MyAppComponent from './MyAppComponent';
// 1. Create the HTTP link to your GraphQL server
const httpLink = createHttpLink({
uri: 'https://your-graphql-api-endpoint.com/graphql', // Replace with your API
});
// 2. Instantiate Apollo Client
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: httpLink,
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});
// 3. Wrap your app with ApolloProvider
const App = () => {
return (
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<MyAppComponent />
</ApolloProvider>
);
};
export default App;Step 4: The Magic Part: Querying Data
Now, let’s fetch some data! We use the useQuery hook.
javascript
// UserProfile.js
import React from 'react';
import { View, Text, FlatList, ActivityIndicator } from 'react-native';
import { useQuery, gql } from '@apollo/client';
// Define your query with gql
const GET_USER_PROFILE = gql`
query GetUserProfile($userId: ID!) {
user(id: $userId) {
name
email
posts(limit: 3) {
id
title
body
comments {
id
text
author {
name
}
}
}
}
}
`;
const UserProfile = ({ userId }) => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_USER_PROFILE, {
variables: { userId: userId },
});
if (loading) return <ActivityIndicator size="large" />;
if (error) return <Text>Error: {error.message}</Text>;
const { user } = data;
return (
<View>
<Text>Name: {user.name}</Text>
<Text>Email: {user.email}</Text>
<Text>Recent Posts:</Text>
<FlatList
data={user.posts}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.id}
renderItem={({ item }) => (
<View style={{ marginVertical: 10 }}>
<Text style={{ fontWeight: 'bold' }}>{item.title}</Text>
<Text>{item.body}</Text>
<Text>Comments: {item.comments.length}</Text>
</View>
)}
/>
</View>
);
};
export default UserProfile;See that? One query. One network request. We got a user, their posts, and the comments on each post. This is the power move.
Step 5: Mutations (Creating/Updating Data)
Fetching is cool, but you need to write data too. That’s where mutations come in.
javascript
// CreatePost.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { Button, TextInput, View } from 'react-native';
import { useMutation, gql } from '@apollo/client';
const CREATE_POST = gql`
mutation CreatePost($title: String!, $body: String!) {
createPost(input: { title: $title, body: $body }) {
id
title
body
}
}
`;
const CreatePost = () => {
const [title, setTitle] = useState('');
const [body, setBody] = useState('');
const [createPost, { data, loading, error }] = useMutation(CREATE_POST, {
// Optional: Refetch related queries after mutation
refetchQueries: ['GetUserProfile'],
});
const handleSubmit = () => {
createPost({ variables: { title, body } });
setTitle('');
setBody('');
};
return (
<View>
<TextInput placeholder="Title" value={title} onChangeText={setTitle} />
<TextInput placeholder="Body" value={body} onChangeText={setBody} multiline />
<Button title={loading ? "Posting..." : "Create Post"} onPress={handleSubmit} disabled={loading} />
{error && <Text>Error creating post: {error.message}</Text>}
</View>
);
};Real-World Use Cases: Where GraphQL Shines in Mobile Apps
Social Media Feeds: The classic example. A single screen needs user info, a feed of posts, comments, likes, and follower counts. One GraphQL query can orchestrate this complex data graph perfectly.
E-commerce Apps: A product page needs product details, variants, reviews, related products, and inventory status. A tailored query prevents fetching the entire product catalog.
Dashboard & Analytics Apps: Users can select specific metrics and date ranges. The GraphQL query can dynamically adjust to request only the selected data points, making it highly efficient.
Best Practices to Keep You Sane
Use Code Generation: Tools like
graphql-code-generatorcan automatically generate TypeScript types and React hooks from your GraphQL operations. This catches errors at compile time and gives you killer autocomplete. Trust me, it’s a lifesaver.Leverage Apollo Cache: Apollo Client’s normalized cache is incredibly smart. Learn how to update it after mutations (
updatefunction) to keep your UI instantly responsive.Implement Pagination: Don’t fetch 10,000 items at once. Use GraphQL cursor-based or offset-based pagination with
fetchMorefor infinite scroll.Handle Errors Gracefully: GraphQL can return partial data. Always check for
errorsin the response and design your UI to handle degraded states.Secure Your Endpoint: Use authentication tokens via headers and implement query depth/ complexity limiting on your server to prevent malicious, overly complex queries.
FAQs (Stuff You’re Probably Wondering)
Q: Is GraphQL a replacement for REST?
A: Not necessarily a replacement, but a compelling alternative for complex, data-heavy applications, especially where network performance is key (like mobile). Many companies use both.
Q: Doesn’t it make the frontend more complex?
A: Initially, there’s a learning curve. But once you’re past it, it reduces complexity by centralizing data fetching logic and eliminating the glue code needed to stitch together multiple REST calls.
Q: What about file uploads?
A: The GraphQL spec doesn’t handle files directly. The common practice is to use a dedicated REST endpoint for uploads or leverage libraries like graphql-upload on the server.
Q: Is it suitable for all projects?
A: For simple apps with few, stable data requirements, REST might be simpler. GraphQL’s value skyrockets with increasing data and UI complexity.
Conclusion: Should You Jump Onboard?
If your React Native app is dealing with interconnected data, needs to be performant on shaky mobile networks, and you want to move fast without constantly bugging your backend team for new endpoints—then yes, GraphQL is absolutely worth it.
The initial setup and conceptual shift require some investment, but the payoff in developer productivity, app performance, and overall flexibility is massive. Start by integrating it into a new feature or a smaller project to get a feel for the workflow.
Mastering modern data-fetching techniques like GraphQL is what separates hobbyists from professional developers. It’s a highly sought-after skill in the industry. To learn professional software development courses such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack with in-depth modules on cutting-edge tools like GraphQL, React Native, and more, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. We build the curriculum the industry actually needs.
So, are you ready to ditch the data waterfalls and start declaring your data needs with precision? Give GraphQL a try in your next React Native project. Your future self (and your users) will thank you.