Build a Real-Time Chat App: A No-Sweat Firebase Tutorial
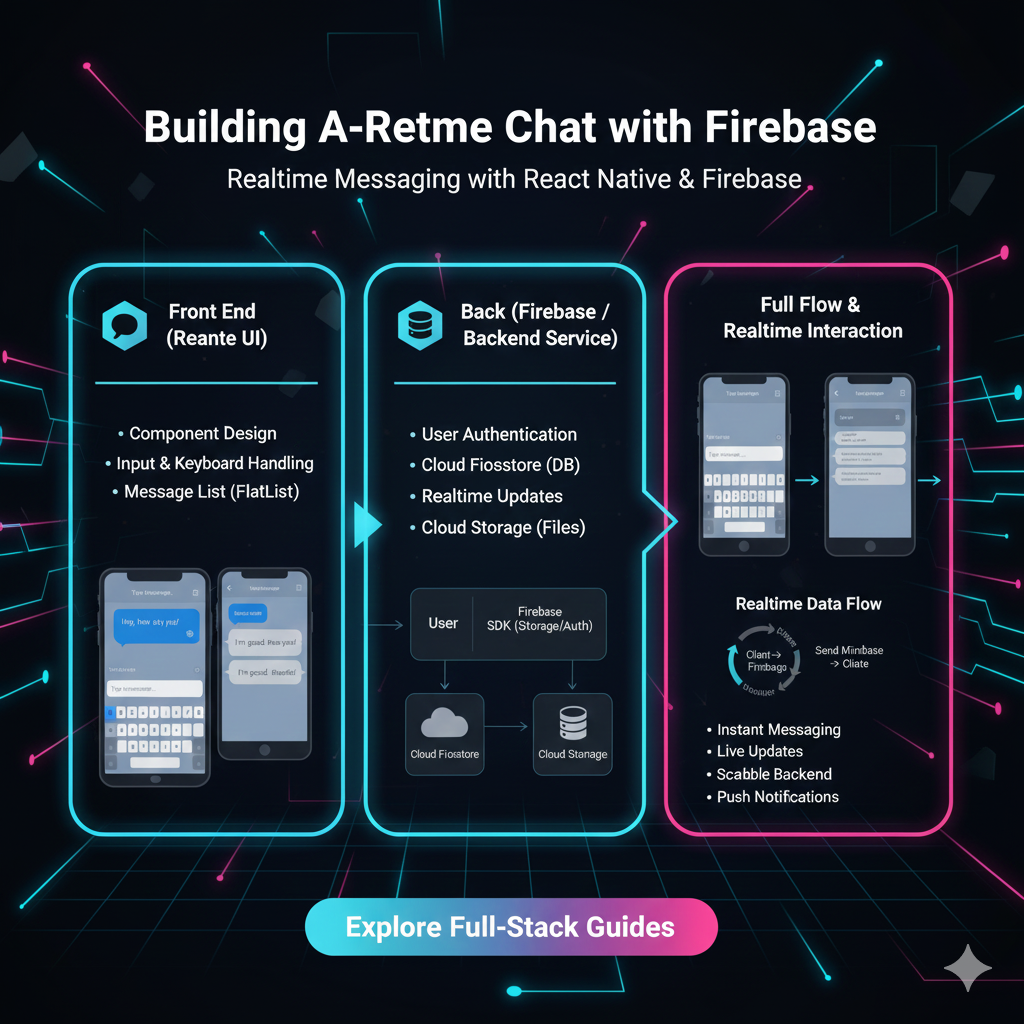
Want to build a real-time chat app like WhatsApp or Slack? This step-by-step Firebase tutorial covers Firestore, Authentication, and security rules to get you live in no time. Level up your skills with CoderCrafter!
Ever been on a site like WhatsApp Web or in a Slack channel and marveled at how messages just pop in instantly, without you ever hitting refresh? That magic is called real-time functionality, and for the longest time, it was a complex, server-heavy nightmare to build.
But what if I told you that you can build your own sleek, real-time chat application without managing a single server? Yeah, you read that right. No configuring WebSockets, no complex backend code. The secret sauce? Google Firebase.
In this deep dive, we're not just scratching the surface. We're building a fully functional chat app, talking best practices, and unpacking the core concepts so you can apply this power to your own projects. Let's get this bread! 🚀
Why Firebase is a Game-Changer for Real-Time Apps
In a nutshell, Firebase is a Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform. Think of it as a massive toolbox in the cloud that hands you pre-built, powerful features so you can focus on building the front-end experience your users will love.
For real-time chat, two tools in this toolbox are absolute rockstars:
Cloud Firestore: A super-flexible, NoSQL database that syncs data in real-time across all connected clients. When one user sends a message, Firestore shouts, "Hey, everyone, there's a new message!" and all other listening apps instantly update.
Firebase Authentication: A secure and easy way to add user logins. We don't want anonymous trolls in our chat app, right? This handles sign-in with Google, Email/Password, and more.
Real-World Use Cases (It's Not Just Chat!)
While we're building a chat app, this real-time tech is everywhere:
Live Collaboration: Google Docs, Figma, where multiple people edit simultaneously.
Live Dashboards: Tracking Uber rides, stock prices, or sports scores.
Multiplayer Games: Syncing player positions and game state in real-time.
Delivery Tracking: The map that shows your food getting closer.
Building Our Real-Time Chat: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
We'll be using vanilla JavaScript to keep things universal, but these concepts apply directly to React, Vue, Angular, or any other framework.
Step 1: Set Up Your Firebase Project
Head over to the Firebase Console.
Click "Add project", give it a name (like
my-awesome-chat), and follow the setup steps.Once created, click on "Firestore Database" from the sidebar and then "Create database". Start in test mode for now (we'll lock it down later).
Step 2: The Basic HTML Structure (index.html)
This is our simple UI. No fancy CSS, just the bones.
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Firebase Chat</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="chat-container">
<div id="user-auth">
<input type="email" id="email-input" placeholder="Your email">
<input type="password" id="password-input" placeholder="Your password">
<button id="sign-in-btn">Sign In</button>
<button id="sign-up-btn">Sign Up</button>
</div>
<div id="chat-room" class="hidden">
<div id="messages-container"></div>
<div class="message-input-area">
<input type="text" id="message-input" placeholder="Type a message...">
<button id="send-btn">Send</button>
<button id="logout-btn">Logout</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Firebase SDKs -->
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/9.22.0/firebase-app-compat.js"></script>
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/9.22.0/firebase-firestore-compat.js"></script>
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/9.22.0/firebase-auth-compat.js"></script>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Step 3: Firebase Configuration & Initialization (script.js)
This is where the magic starts. Go to your Project Settings in the Firebase console and grab your web app's firebaseConfig object.
javascript
// Your web app's Firebase configuration
const firebaseConfig = {
apiKey: "your-api-key",
authDomain: "your-project.firebaseapp.com",
projectId: "your-project-id",
storageBucket: "your-project.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "123456789",
appId: "your-app-id"
};
// Initialize Firebase
const app = firebase.initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
const db = firebase.firestore();
const auth = firebase.auth();Step 4: Authenticating Users
Let's make our sign-up and sign-in buttons work.
javascript
const signUpButton = document.getElementById('sign-up-btn');
const signInButton = document.getElementById('sign-in-btn');
const emailInput = document.getElementById('email-input');
const passwordInput = document.getElementById('password-input');
signUpButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
const email = emailInput.value;
const password = passwordInput.value;
auth.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(email, password)
.then((userCredential) => {
// User signed up successfully
console.log("User signed up:", userCredential.user);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("Error signing up:", error.message);
});
});
signInButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
const email = emailInput.value;
const password = passwordInput.value;
auth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email, password)
.then((userCredential) => {
// User signed in successfully
console.log("User signed in:", userCredential.user);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("Error signing in:", error.message);
});
});
// Listen for auth state changes (user signs in or out)
auth.onAuthStateChanged(user => {
if (user) {
// User is signed in, show chat room.
document.getElementById('user-auth').classList.add('hidden');
document.getElementById('chat-room').classList.remove('hidden');
loadMessages(); // We'll write this function next!
} else {
// User is signed out, show auth form.
document.getElementById('user-auth').classList.remove('hidden');
document.getElementById('chat-room').classList.add('hidden');
}
});Step 5: The Real-Time Magic - Sending & Listening for Messages
This is the core of our app.
Sending a Message:
javascript
const sendButton = document.getElementById('send-btn');
const messageInput = document.getElementById('message-input');
sendButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
const messageText = messageInput.value;
const user = auth.currentUser;
if (messageText.trim() === "" || !user) return;
// Add a new document to the "messages" collection
db.collection("messages").add({
text: messageText,
uid: user.uid,
email: user.email,
timestamp: firebase.firestore.FieldValue.serverTimestamp() // Uses server time for consistency
})
.then(() => {
messageInput.value = ""; // Clear the input
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("Error sending message:", error);
});
});Listening for Messages in Real-Time:
javascript
function loadMessages() {
const messagesContainer = document.getElementById('messages-container');
// This .onSnapshot listener is the heart of real-time updates.
db.collection("messages")
.orderBy("timestamp", "asc") // Order by time
.onSnapshot((querySnapshot) => {
messagesContainer.innerHTML = ''; // Clear current messages (for simplicity)
querySnapshot.forEach((doc) => {
const messageData = doc.data();
// Create a message element and append it
const messageElement = document.createElement('div');
messageElement.classList.add('message');
messageElement.innerHTML = `
<strong>${messageData.email}:</strong> ${messageData.text}
`;
messagesContainer.appendChild(messageElement);
});
// Scroll to the bottom to see the latest message
messagesContainer.scrollTop = messagesContainer.scrollHeight;
});
}Boom! 💥 You now have a working real-time chat. Open it in two different browser windows, sign in with two different users, and watch the messages sync instantly.
Leveling Up: Best Practices You Can't Ignore
Our app works, but it's a bit barebones. Let's talk pro-level stuff.
Security Rules are NON-NEGOTIABLE: Leaving your Firestore in "test mode" is like leaving your house with the door wide open. You MUST set up security rules. Here's a basic one for our chat app:
javascript
rules_version = '2'; service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { // Allow users to read/write only if they are logged in match /messages/{document} { allow read, create: if request.auth != null; } } }You can set these in the Firestore "Rules" tab. This rule ensures only authenticated users can read and send messages.
Structure Your Data for Scalability: For a larger app, you'd want to structure your data better. Instead of just storing the user's email with every message, you might have a
userscollection and store only theuidin the message, fetching the user's profile separately. This is more efficient.Handle Offline States: Firestore has great offline persistence, but your UI should too. You can show a "connecting..." indicator or temporarily store messages locally if the connection is lost.
FAQs: Your Burning Questions, Answered
Q: Is Firebase free?
A: Firebase has a generous free tier (the "Spark Plan") which is perfect for learning and small projects. As you scale, you pay for what you use. Always check their pricing page.
Q: Can I use this with React or Vue?
A: Absolutely! The concepts are identical. Firebase has modular SDKs that work seamlessly with modern frameworks. You'd just use the same onSnapshot listeners and authentication methods inside your useEffect or onMounted hooks.
Q: What about file uploads (like images in chat)?
A: Firebase has you covered with Cloud Storage, another tool in the BaaS toolbox designed specifically for storing user-generated files like images and videos.
Q: This is cool, but how do I build a full, production-ready app?
A: You're thinking like a true developer! Building a complete application involves connecting many more dots: state management, advanced routing, optimized databases, and deployment strategies.
To learn professional software development courses such as Python Programming, Full Stack Development, and MERN Stack, visit and enroll today at codercrafter.in. Our structured programs take you from basics to building complex, industry-ready applications, guiding you on every step of your coding journey.


















